
1. INTRODUCTION
Tagging, annotation of unstructured text data forms the basis of building all machine learning(referred to as ML from here on) solutions around natural language. Page ranking of a content on the internet, discoverability based on a search query, recommending the most appropriate product to buyer on an ecommerce platform is all based on the appropriateness/quality of tags.
2. PROBLEM AND MOTIVATION
2.1 Sunbird
Sunbird is an open source platform that hosts thousands of educational content with a vision of providing learning opportunities to millions of children. The core of the platform is a huge knowledge graph of learners, Content, different frameworks of Concepts and learning objectives.
A Content created by an Author is a node in the graph with certain attributes and relations to other nodes. Different types of Content such as pdf , youtube video, mp4 and html can be created and they form different relations with other entities of the graph such as Language models. Tagging a Content means tagging a Content to its grade, its learning objectives, curriculum and other tags for discovery such as language, difficulty or its purpose. This can be extended to any knowledge graph.
2.2 Machine learning Workbench
Sunbird also comprises a ML Workbench, daggit. The objective of the daggit project is to create a set of tools that can enable adopters to use ML as a viable technique to solve various problems in their ecosystems.
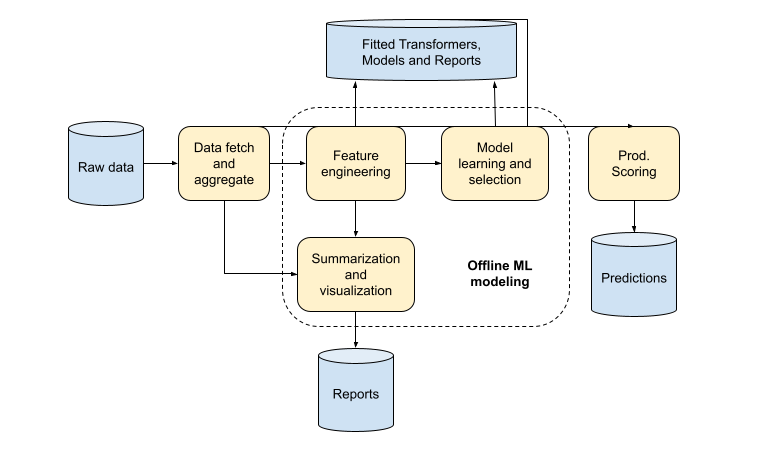
Daggit represents every application as a directed acyclic graph(DAG). It provides tools to integrate with different data sources such as cassandra, elastic search, s3. It also allows to listen to Kafka topics, rest API’s or schedule jobs in batches.A Content created on Sunbird generates a kafka event. This is used as an anchor to initiate tagging process on daggit.
3. BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORK
Several text annotation, keyword extraction services are available for English language. Google natural language api’s, allen NLP api provide competitive text analysis tools such as parts of speech and named entity recognition. But these are services that work on structured, preprocessed English text. The recent AutoML Natural Language tool enables one to create custom machine learning models to classify English text through a supervised approach. This is a step closer to creating tags that are domain specific but still treat it as a supervised text classification and requires creating large training data to be put in production systems.
We propose an approach that is unsupervised and improves over time. Daggit as infra integrates into production systems like a plugin, allows dockerization, distributed computing and data versioning. In the current version, text in all languages are translated to English with language tag. This is done since the third party services used do not support other languages.
4. APPROACH
Auto tagging of text is based on a given taxonomy. This could be a very generic ontology or a taxonomy specific to a domain. In Sunbird use case, we use National curriculum framework as the taxonomy.
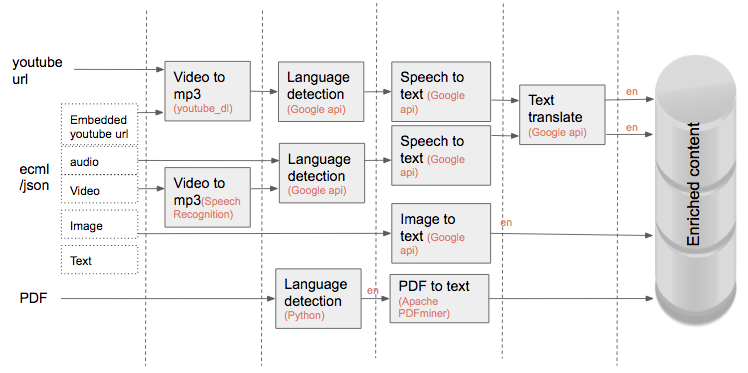
A kafka consumer operator(a node in DAG) listens to a content generation event. This event initiates Content enrichment pipeline(CEP) operator. The detailed steps in Content enrichment is shown in Figure 2. Multiple third party services such as Google speech to text, vision api are used here. The output of the Content enrichment pipeline is another kafka event that contains the following:
Text extracted from different types of Content translated to English Image tags Audio transcript from audio and video files We will refer to this as enriched Content in the remaining of this document. Additional tags for Content quality are being built into the next version of CEP.
The first step in taxonomy tagging is taxonomy flattening. At a prefixed level of the taxonomy graph(ex: textbook chapter Concepts) all the child nodes are aggregated. Taxonomy is then a set of keywords that contains the information of the structure from which it is derived.
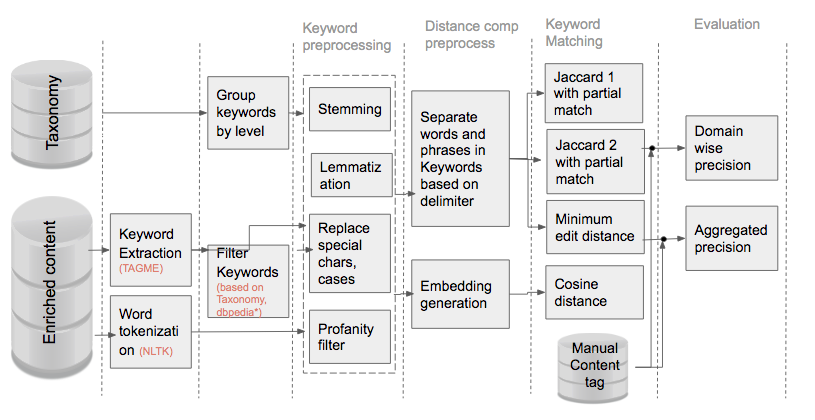
From the enriched text, keywords are extracted using TAGME api (built on DBpedia corpus). Taxonomy and the enriched text keyword goes through similar preprocessing as shown in Figure 3. Different preprocessing methods can be configured on the DAG.
Once the keywords from both taxonomy and Content are available this is a document similarity problem. Both embedding based model operators as well as statistical similarity computation operators such as jaccard distance or minimum edit distance is built into daggit.
Result:
Auto tagging DAG is tested in real time on Sunbird.Based on the length and type of multimedia present in the Content upto 2minutes(for youtube video of 25 minutes) of processing time is required.
On a manually curated corpus of 2000 Content in Hindi and English, using jaccard Index a precision of 64% is achieved. This architecture allows rapid experimentation and comparison of results on production data using different models. The model efficiency as well as down time is expected to improve by using embedding based approaches. Integrating feedback from the user in improving the models is also planned for the next version.
5. CONTRIBUTION
The following are the major contribution of this work:
Developing an open source platform daggit that allows to create, collaborate and consume ML tools and processes. Using a plugin architecture to develop a text auto tagging on daggit that integrates with production systems. Developing an ML based ensemble approach of mapping a text to any given taxonomy for English language.
REFERENCES